Why Refactoring Your Apps is a Smarter Move for the Cloud
.webp?width=941&height=492&name=4%20(2).webp)
Ever tried lifting-and-shifting an old enterprise app to the cloud only to end up with more headaches, such as random crashes, crazy bills, and constant patching? And at that moment you realize that something’s missing. That ‘something’ is refactoring. Think of it as giving your apps a tune-up, making the engine run smoother, the navigation simpler, and enhancing the overall reliability before your cloud innovation.
Refactoring enterprise applications before moving them to the cloud helps modernization and future-proofs business operations. Restructuring internal code and architecture unlocks cloud-native capabilities, transforming legacy assets into agile, scalable, and cost-efficient solutions.
For instance, in the healthcare industry, refactoring patient management systems helps enhance security and performance by restricting sensitive data access to authorized users, while supporting remote healthcare services. Cloud integration scales these systems to accommodate telemedicine and flexible care delivery, moving beyond the limits of traditional centralized software.
Why Start With Refactoring?
Moving apps to the cloud works best when they are lean, reliable, and modular. Refactoring first removes technical debt and positions applications to use the cloud’s strengths. Teams spend less time troubleshooting and more time building features and responding to business needs.
When preparing for a cloud migration, focus on cleaning up and organizing apps. This can set your business up for better performance, lower risk, and greater agility, ready for future challenges and opportunities.
Refactoring makes your enterprise fit for the new era.
What Does Refactoring Imply for Enterprises?
Refactoring means cleaning up code, splitting massive structures into precise independent services, and simplifying how various components in the application interact. Users see familiar screens and workflows, but the core is easier to maintain, update, and scale. As part of refactoring, you must:
- Update coding patterns
- Separate key functions
- Upgrade libraries and frameworks
Streamlining enables teams to focus on developing new features, reducing the time being spent on fixing old problems.
For instance, retailers benefit by splitting their e-commerce platforms into distinct modules for product catalog, checkout, and shipping, enabling each part to scale independently. This means smoother performance during peak shopping times and significant cost savings when traffic drops; all while enabling faster deployment of new features and bug fixes.
How Does Refactoring Help the Cloud?
Cloud infrastructure favours flexibility and instant scaling. Refactoring positions your application to benefit from:
- Cost savings due to lower maintenance and reduced overuse of resources: Refactored apps use cloud capacity more efficiently, so you only pay for the resources that you need. Maintenance costs drop as codebase complexity decreases, and fewer resources are wasted on unused or duplicated components.
- Faster performance and improved reliability for users: Optimizing core logic and splitting up workloads lets your app scale easily to meet demand, delivering quicker response times during peak and off-peak periods. Users experience fewer outages as resilient, cloud-ready services take over in case of failures.
- Enhanced security compliance, especially in regulated industries: Migrating to modern authentication, encryption, and role management during refactoring strengthens your security framework. This makes it easier to meet industry mandates and reduce risk in sectors like finance and healthcare.
- Improved productivity through modular applications and easier updates: Removing outdated code and adopting modular architecture creates a cleaner environment for development. Developers spend less time troubleshooting legacy issues and focus more on meaningful improvements or new features.
- Better adaptability for new platforms and technologies: Modernized refactored code integrates seamlessly with cloud-native services and APIs. This helps your business pivot quickly when adopting new channels, devices, or shifting to new market opportunities.
- Reduced technical debt, eliminating layers of outdated code: Technical debt drops as old dependencies are weeded out. This means less firefighting and faster delivery times for updates, compliance, and innovation projects. Refactoring sets a foundation for ongoing business growth and responsiveness.
Small Efforts for Big Improvements
Refactoring helps organizations unlock the full potential of cloud migration in many practical ways. For example, when finance apps are concerned, breaking down a monolithic payments system into smaller microservices can improve transaction speeds and reduce outages, making the system more reliable and easier to update as regulations evolve.
This modular structure enables teams to make changes to specific components without disrupting the entire application, ensuring smooth operations during transformation.
Companies focused on analytics see improvements by refactoring complex dashboards into faster, reusable components. The resulting instant responsiveness provides up-to-date insights that empower decision-makers to act quickly based on real-time data.
These use cases highlight how refactoring prepares systems to be faster, more scalable, and get easier to maintain for thriving in dynamic cloud environments.
Following the Best Practices
Successful application modernization starts with a deep understanding of your existing codebase. It is recommended to use automated code analysis tools to map dependencies and identify areas causing complexity or performance issues.
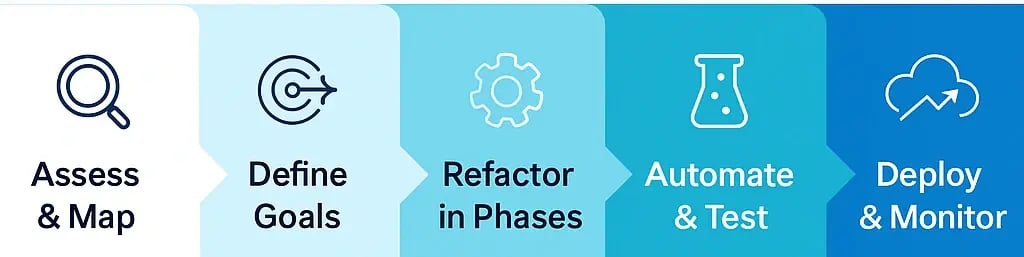
- Define the goals of refactoring clearly, such as improving maintainability, enhancing scalability, or preparing for cloud migration.
- Break down the refactoring process into small, manageable chunks that allow for incremental improvements.
- Test frequently and automate these tests to ensure changes do not break existing functionality.
- Keep refactoring separate from feature development or bug fixes to maintain focus and clarity.
- Maintain updated documentation throughout the process to help your teams stay aligned and assist future developers.
- Regular peer reviews help identify issues early, encourage knowledge sharing, and improve code quality.
- Plan your deployment strategy carefully, releasing refactored components gradually, while monitoring their impact.
Refactoring is a continuous process rather than a one-time project to ensure your applications remain flexible, efficient, and secure as requirements evolve. With these practices handy, refactoring apps and cloud migration becomes smoother. It minimizes risk and maximizes the benefits of refactoring for your enterprise applications.
Covasant’s rapid application modernization services help streamline transformation, reduce technical debt, and build cloud-native, scalable enterprise applications with speed and security. Explore smarter, phased modernization approaches tailored for your enterprise needs.
Talk to us to learn more about Covasant’s AI-led rapid application modernization services.



